Multiscale SBFEM analysis
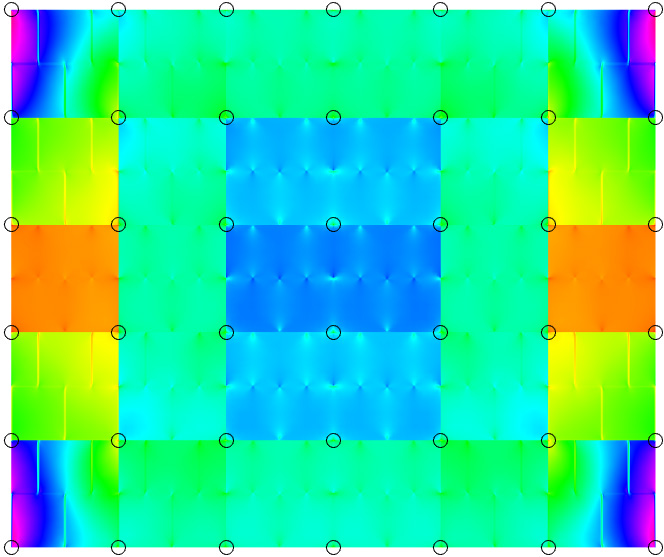
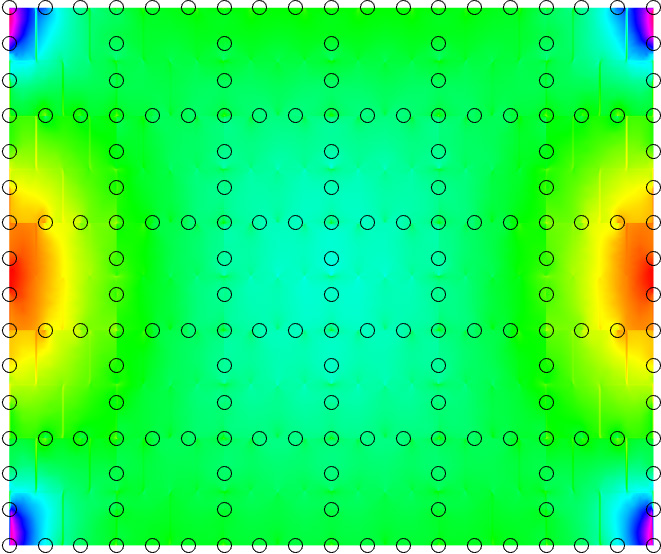
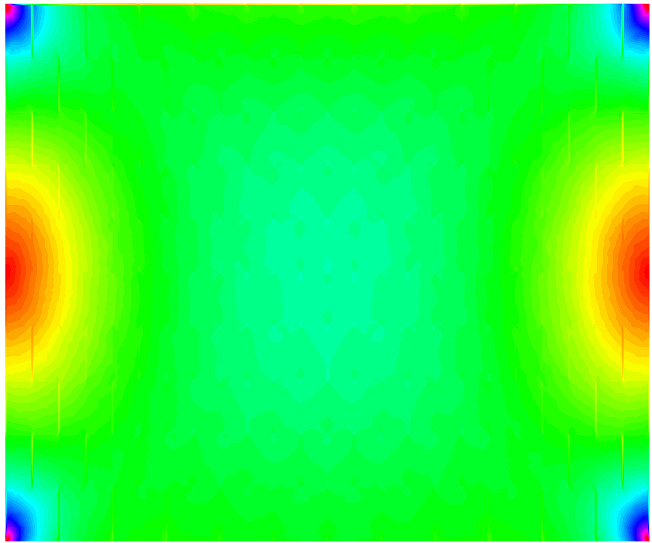
Real world structures pose a significant computational challenge. A methodology to circumvent this issue is the introduction of multiscale methods. Here, we propose exploiting SBFEM on the fine scale to account for damage related phenomena and solve the governing equation on a significantly reduced coarse mesh of representation volume elements (RVEs). These scales are linked with numerically computed mapping functions according to the extended multiscale finite element method, which are only computed once at the start of analysis. Hence, we call this approach the multiscale scaled boundary finite element method (MsSBFEM).
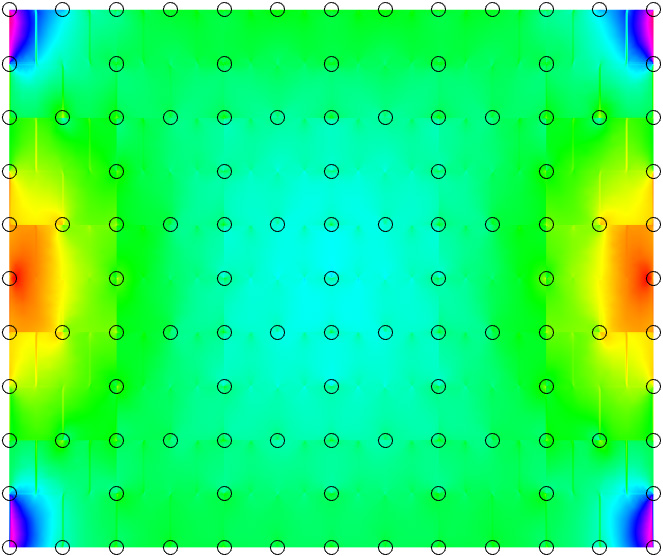
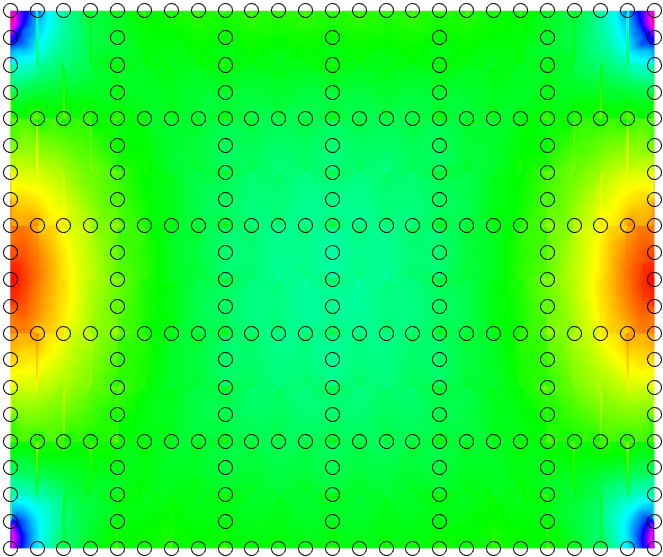
The behaviour of different types of RVEs possesing either 4/8/12/16 coarse nodes using the example of a masonry wall is explored.
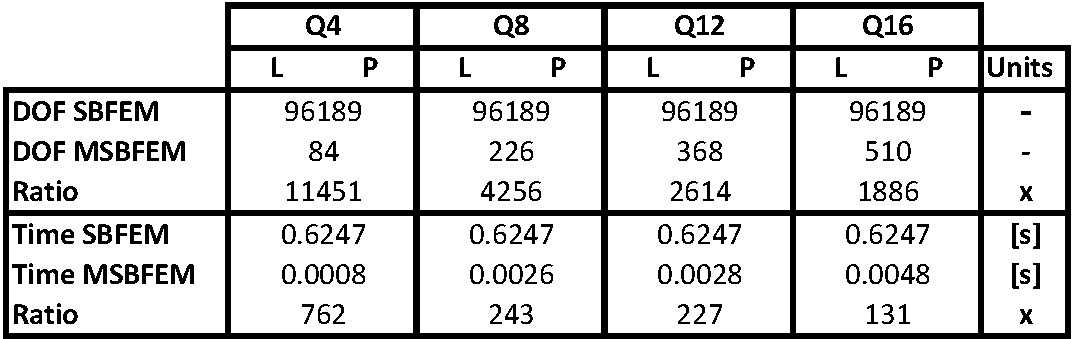
Computational gains
Substantial computational gains can be achieved, when utilizing multiscale methods, while maintaining most of the model's fidelity.